Thermostatic expansion valves
What is Thermostatic expansion valve?
One of the types of expansion valves in the refrigeration industry is the thermostatic expansion valve. As you know, the function of the expansion device in the refrigeration cycle is to adjust the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator. This is done base on superheat control. With increasing of the evaporator load and amount of the superheat, the valve opens and if it decreases, the expansion valve closes. In the thermostatic expansion valve, the above process is done mechanically according to differential of pressure.

Main components of Thermostatic expansion valves
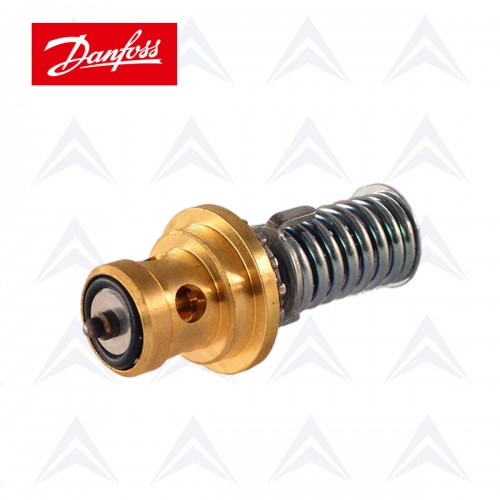
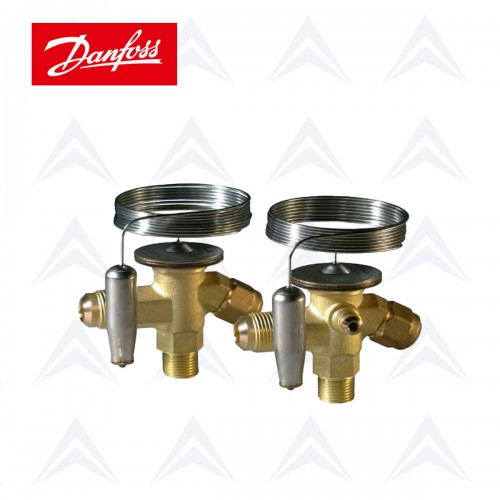
The main components of the thermostatic expansion valves include the body, sensing thermal bulb, flexible diaphragm, orifice, spring, superheat adjustment screw, and inlet and outlet connections.
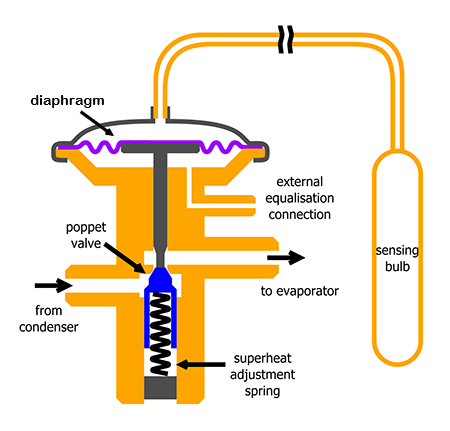
How thermostatic expansion valves work?
When the load on the evaporator increases, the refrigerant evaporates at a faster rate and the temperature of the gas leaving the compressor rises (increasing superheat). Since the thermostatic expansion valve bulb is installed on the suction line and at the outlet of the evaporator, the refrigerant charged inside it is at the same temperature as the system refrigerant, and as the temperature of the system refrigerant increases, the temperature and, as a result, the pressure of the bulb also increases. As the valve pressure increases, its force enters the diaphragm through the capillary tube and pushes it down. As the diaphragm goes down, the orifice opens the refrigerant flow path and the expansion valve allows more refrigerant to be injected into the evaporator.
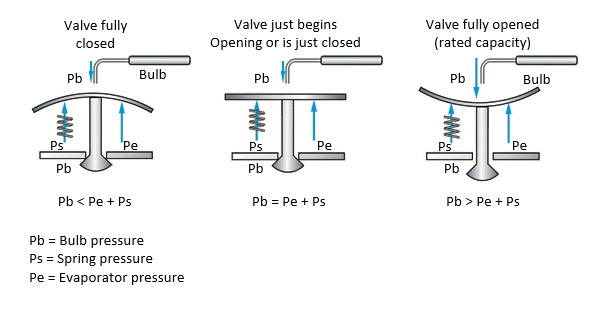

As a result, the refrigerant volume inside the evaporator and the evaporator pressure increases and the diaphragm moves upwards. By increasing the volume of refrigerant inside the evaporator, the temperature of the compressor suction gas, superheat and therefore the temperature of the bulb decreases. By reducing the diaphragm bulb pressure, it moves down and by closing the expansion valve, a smaller volume of refrigerant is injected into the evaporator. This situation continues until the balance is established and the spring reaches the initial adjustment position and set point superheat. If the evaporator load decreases, the above cycle is repeated in reverse.
Maximum operation pressure or MOP in thermostatic expansion valves
There are two types of thermal bulb in thermostatic expansion valves: Liquid charged bulb and MOP bulb.
Liquid charged bulb
In the thermostatic expansion valve equipped with liquid charging bulb, a large volume of two-phase refrigerant mixture is charged inside the bulb. Since there is always liquid inside the bulb, as the liquid evaporates and the volume of steam increases, as long as the superheat increases, the pressure of the bulb also increases. In the previous systems, the refrigerant inside the bulb was same as the refrigerant of the system (Parallel-charged), but today, cross-charged or using of different refrigerants in bulb is more common.
MOP bulb
In the bulb with MOP charging, the volume of liquid is more limited and with the increase in pressure and temperature of the suction line, all the liquid inside the bulb evaporates upon reaching a specific and pre-set pressure. As a result, increasing the suction pressure has no effect on increasing the valve pressure and the expansion valve will not open more. In fact, this limited pressure and its corresponding temperature is the maximum pressure and working temperature of the evaporator.
The reason for using the thermostatic expansion valve with MOP charge is to prevent the overload of the compressor, especially at the initial start and when the evaporator pressure is higher than normal operation conditions.
Equalizer in thermostatic expansion valve
Thermostatic expansion valves base on models includes internal or external equalizer.
Thermostatic expansion valve with external equalizer
One of the forces acting on the diaphragm of the thermostatic expansion valve is the force caused by the evaporator pressure, which acts against the direction of the pressure of the expansion valve bulb and balances the valve while adjusting the superheat. In the thermostatic expansion valve with an external equalizer, the above pressure is the outlet pressure of the evaporator. In this way, an equalizing pipe is connected from the outlet of the evaporator to the equalizing port of the valve.
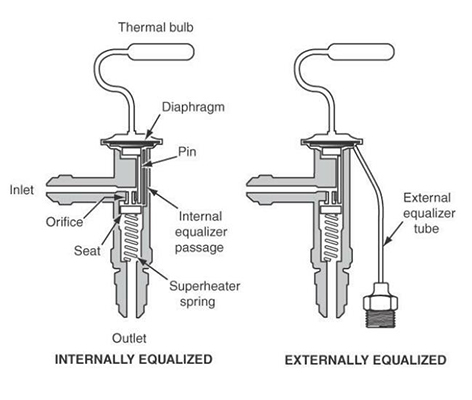
Thermostatic expansion valve with internal equalizer
In the internal equalizer thermostatic expansion valve, the output pressure of the expansion valve is the criterion and does not consider the pressure drop of the evaporator. This type of valve is used in refrigeration systems where the evaporator has minimum pressure drop and does not have a distributor, and due to this limitation, the use of external equalizer is much more common in the refrigeration market.
Aljebal, supplier of all of Danfoss, Alco and Parker-Sporlan thermostatic expansion valves in Dubai, UAE.





